Introduction ROI (Return on Investment).
Return on Investment (ROI) is one of the most widely used metrics in both business and finance. It plays a crucial role in decision-making by evaluating the profitability and efficiency of an investment. Whether you’re a business owner assessing marketing strategies or an individual managing your portfolio, understanding ROI is essential for maximizing profits and optimizing resource allocation.
In this article, we’ll delve deep into what ROI is, how it’s calculated, its importance, various types of ROI, its advantages and disadvantages, and real-world examples to illustrate its application. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of ROI and how it can benefit your financial and business decisions.
What is ROI (Return on Investment).?
ROI, or Return on Investment, is a performance metric used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or compare the efficiency of multiple investments. It is expressed as a percentage and indicates the return generated from an investment relative to its cost.
The basic idea behind ROI is to measure the profitability of an investment by comparing the returns generated to the initial cost. A higher ROI indicates a more successful investment.
Formula for Calculating ROI (Return on Investment).
The most common formula to calculate ROI is as follows:
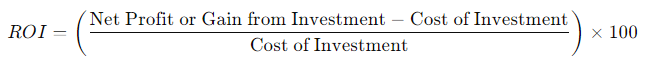
This formula calculates the percentage return on an investment by subtracting the cost of the investment from the net gain, then dividing it by the cost of the investment.
Example:
Imagine you invested $5,000 in a marketing campaign, and as a result, your business earned $7,000 in additional revenue. The ROI calculation would be:
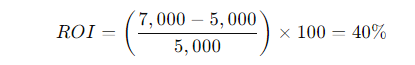
This means the marketing campaign yielded a 40% return on your investment.
Importance of ROI (Return on Investment).
ROI is an essential metric because it provides insight into the profitability and effectiveness of investments. Here are some key reasons why ROI is crucial for businesses and individuals alike:
1. Performance Evaluation
ROI helps evaluate the performance of investments or business ventures. Whether you’re launching a new product, running a marketing campaign, or investing in stocks, ROI offers a clear indicator of how well your investment is doing.
2. Comparing Investments
ROI allows you to compare different investments or projects. By calculating the ROI for multiple options, you can identify which investment offers the highest return and is worth pursuing.
3. Resource Allocation
Businesses can use ROI to allocate resources efficiently. For example, a company may decide to invest more in high-ROI activities like digital marketing while scaling back on low-ROI initiatives.
4. Risk Management
High-risk investments often come with the potential for high returns. Calculating ROI helps in evaluating whether the return is worth the risk, aiding in better risk management.
5. Investor Confidence
Companies with consistently high ROI tend to attract more investors. Investors often use ROI to assess the profitability of a company or project before committing funds.
Types of ROI (Return on Investment).
There are different ways to measure ROI depending on the context. Here are some of the common types of ROI that are used across industries:
1. Financial ROI (Return on Investment).
This is the traditional form of ROI that measures the financial gains or losses generated from an investment. It is often used in stock market investments, real estate, and other financial ventures.
2. Marketing ROI (Return on Investment).
Marketing ROI measures the effectiveness of a marketing campaign. Businesses use this type of ROI to determine whether their marketing efforts, such as advertising, social media campaigns, or SEO, are providing a good return on the money spent.
Formula:
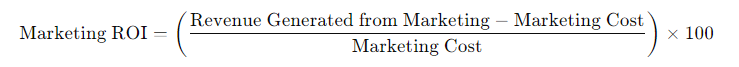
3. Social Media ROI (Return on Investment).
A subcategory of marketing ROI, this measures the returns generated from social media platforms. It focuses on metrics like engagement, reach, and conversion rates to determine the impact of social media efforts.
4. Employee ROI (Return on Investment).
Employee ROI measures the productivity or profit generated by employees relative to their cost (salaries, benefits, etc.). It’s useful for assessing whether the human resources in a company are effectively contributing to overall profitability.
5. ROI (Return on Investment) in Real Estate
In real estate, ROI is used to measure the profitability of a property investment. It takes into account factors such as property value, rental income, and maintenance costs to determine whether the property is generating a good return.
Formula:
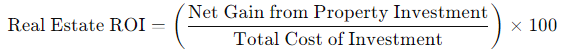
6. ROI (Return on Investment) in Education
This type of ROI assesses the return on investing in education, such as the value of a college degree or professional certifications. The focus is on comparing the cost of education to the financial benefits gained from increased earning potential.
Advantages of ROI (Return on Investment).
1. Simple and Easy to Use
One of the biggest advantages of ROI is its simplicity. It provides a straightforward way to calculate and understand the profitability of an investment.
2. Versatile
ROI can be applied to virtually any type of investment, whether it’s financial, marketing, real estate, or human capital. This makes it a versatile tool across various industries.
3. Universal Metric
Because ROI is expressed as a percentage, it allows easy comparison between different investments, regardless of the industry or scale of investment.
4. Time-Sensitive
ROI can be calculated over different time periods, offering flexibility in evaluating both short-term and long-term investments.
Disadvantages of ROI (Return on Investment).
Despite its many benefits, ROI has some limitations:
1. Ignores Time Factor
One of the key drawbacks of ROI is that it doesn’t consider the time value of money. For instance, an investment yielding 20% ROI in one year is not the same as one generating 20% over five years. Without accounting for time, comparisons between long-term and short-term investments may be misleading.
2. Doesn’t Account for Risk
ROI doesn’t factor in the risk associated with an investment. High-ROI investments might be more volatile or risky, which isn’t reflected in the metric.
3. Not Comprehensive
ROI focuses solely on monetary gain and does not account for intangible benefits such as brand equity, customer satisfaction, or employee morale, which may also contribute to an investment’s success.
4. Can Be Manipulated
Depending on how costs or gains are measured, ROI calculations can sometimes be skewed. For example, businesses might overestimate returns or underestimate costs to make an investment appear more profitable than it is.
Real-World Examples of ROI
1. Digital Marketing Campaign
A company invests $10,000 in a digital marketing campaign and generates $15,000 in additional sales. The ROI for the campaign is:
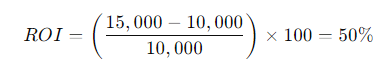
This means the campaign was successful, generating a 50% return on the initial investment.
2. Stock Market Investment
An investor buys shares worth $20,000 and after one year, the shares are worth $24,000. The ROI is:
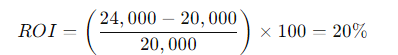
3. Real Estate Investment
An individual purchases a rental property for $200,000 and earns $10,000 per year in rental income. After five years, they sell the property for $240,000. The total gain is:
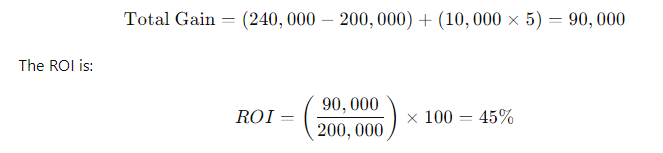
Maximizing ROI
To maximize ROI, consider the following strategies:
1. Optimize Costs
Reducing unnecessary costs is one of the most effective ways to improve ROI. This can be achieved by negotiating better rates with suppliers, reducing operational expenses, or using more cost-effective marketing channels.
2. Focus on High-ROI Activities
In business, it’s essential to identify the activities that yield the highest return. For example, if certain marketing campaigns consistently generate high returns, focus more resources on those areas.
3. Use Data-Driven Decisions
Data and analytics can help optimize investments by identifying trends, opportunities, and areas for improvement. Leveraging tools that track the performance of investments can lead to better decision-making and higher ROI.
4. Manage Risks
Diversifying your investments can help manage risks and ensure a steady ROI. High-risk investments can potentially offer high returns but may also result in significant losses, so it’s important to balance risk and reward.
Conclusion
Return on Investment (ROI) is a crucial metric for evaluating the profitability and effectiveness of investments across various fields, from business ventures to personal finance. Its versatility and simplicity make it an invaluable tool for comparing different opportunities and making informed financial decisions. However, it’s essential to recognize its limitations and complement it with other metrics like the time value of money and risk analysis for a holistic view of investment performance.
By understanding ROI and how to calculate and interpret it, you can make better choices that maximize returns and ensure long-term success in your business or financial ventures.


